The physician uses the term humeral shaft fracture to describe a bone fracture that occurs in the humeral shaft area. Due to the anatomy of the upper arm and the proximity to the nerves (radial nerve) and blood vessels, different problems can very well arise – in the context of the treatment of the injury. However, the prognosis is mostly positive; Complications rarely or never occur during treatment.
What is a humeral shaft fracture?
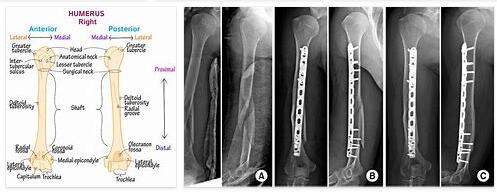
According to abbreviationfinder, the humeral shaft fracture (also known as a humeral shaft fracture, upper arm shaft fracture or diaphyseal humeral fracture ) describes the fracture of the humerus or upper arm bone. The bone in the shaft area (diaphysis) breaks.
Due to the surrounding blood vessels and nerves, the treatment of the fracture is not uncomplicated, although accompanying injuries can sometimes occur, which aggravate the severity of the injury.
Causes
A fracture of the humeral shaft can occur as a result of direct violence (traffic accident, blow). However, indirect effects of violence (falls, twisting) are also possible causes of a humeral shaft fracture. It should be noted that the course of the accident certainly has an influence on the shape of the fracture.
This is because while torsional or spiral fractures usually occur as a result of indirect impacts of violence, piece and transverse fractures are possible in the context of direct impacts of violence. The rubble zone also expands, so that direct acts of violence sometimes cause greater damage than indirect acts of violence. Only very rarely can a humeral shaft fracture also represent an open fracture; Statistically speaking, 6.3 percent of all humeral shaft fractures are so-called “open fractures”.
The course of the accident also has an enormous impact on possible accompanying injuries. If there is a direct trauma, the muscles and also the subcutaneous fatty tissue can be injured. There may be bleeding or tearing of muscle cords. Sometimes compartment syndrome can also be triggered.
For this reason, the physician must also be careful to consider any other injuries that may have occurred as part of the humeral shaft fracture.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
The formation of a swelling is classic. A bruise also accompanies the swelling. The patient also complains of severe pain and a simultaneous restriction of movement. If the nerves (radial nerve) are injured, the so-called “hand drop” occurs. This means that the patient can no longer stretch his hand. In around 20 percent of all cases, the radial nerve is also injured.
If there is an indirect trauma, it must be assumed that the nerve has been pulled. Rupture of the nerve or multiple nerves is rarely diagnosed. Sometimes the nerves can also be “skewered” – due to the bone fracture end. During the reduction (alignment of the fracture) it is quite possible that injuries can occur due to the anatomical conditions. For this reason, the reduction should be carried out extremely carefully.
Diagnosis & disease progression
If a humeral shaft fracture is suspected, the doctor makes a clinical diagnosis. The main focus is on the mobility or immobility of the shoulder and elbow joint, any pain in the fracture area and also on the consideration of crepitations (crunching).
Those clinical clues are unequivocal information that a humeral shaft fracture is present. Nevertheless, the patient is x-rayed so that the diagnosis can be confirmed on the one hand and the extent of the injury can be recognized on the other. The course of the fracture is also decisive for further therapy, so that an X-ray must always be taken. Only in very few cases are further examinations – such as a computer tomography – prescribed so that any joint involvement can be ruled out or diagnosed.
As part of the clinical examination, the doctor also pays attention to the nerve supply to the hand and forearm and also checks the blood circulation. The radial nerve in particular is examined for possible injuries due to the frequency of injuries in humeral shaft fractures. Any damage to the radial nerve can be visualized using EMG. The course of the disease and the prognosis are positive.
It does not matter whether the doctor decides on a conservative or surgical method or whether there was an indirect or direct impact that caused a humeral shaft fracture. Depending on any accompanying injuries, the healing processes can be delayed, so that the top priority in therapy is patience.
Complications
The fracture primarily causes relatively severe pain in the affected area and usually also swelling. The person concerned suffers from restricted mobility, which can often lead to psychological problems. The everyday life of the patient is also made considerably more difficult by these limitations and pain.
If there is pain at rest, it can also lead to sleep problems. In general, the severe pain associated with a humeral shaft fracture leads to irritability. In most cases, a quick diagnosis is possible, so that early treatment can also occur. There are no special complications during treatment. A cast is placed around the affected area to keep it from moving and the affected person must wait for the fracture to heal.
Complications can arise if the humeral shaft fracture is left untreated or the patient exposes himself to unnecessary stress during healing. In severe cases, surgical interventions are also necessary. Life expectancy is not changed by the humeral shaft fracture. Furthermore, after healing, the affected person can usually use the affected area.
When should you go to the doctor?
In the case of a humeral shaft fracture, a doctor must be consulted in any case. If this fracture is not treated by a doctor, in the worst case it can lead to incorrect fusion of the bone, so that surgical intervention is necessary for treatment. The doctor should be consulted for the humeral shaft fracture if the affected person suffers from severe pain and swelling in the respective region. An examination by a doctor should therefore be carried out, especially after an accident or after a violent impact.
Furthermore, limitations in movement point to the humeral shaft fracture. The fracture can also damage nerves, leaving people with numbness in the hand. In many cases, the injury is clearly visible, so no additional examination is necessary for diagnosis. In an acute emergency, the hospital can be visited or an ambulance can be called for the humeral shaft fracture. However, the general practitioner can also identify this bone fracture and continue to treat it. As a rule, the course of the disease is positive and there are no further complications.
Treatment & Therapy
In almost all cases, the doctor treating you decides on conservative treatment. The doctor puts on a so-called Gilchrist bandage; sometimes an ordinary upper arm cast can also be missed. The bandage or cast is worn for about two weeks. The condition of the fracture is then checked and, if necessary, the bandage or cast is applied for another week or two.
However, if there is damage to the vessels, the physician prefers to opt for the surgical method. Conservative treatment is not promising, especially if nerves or soft tissues have been injured or if there is an open fracture. Surgery is also performed on bilateral fractures or a so-called interposition of soft tissue that has been identified in the fracture gap.
In the context of defective fractures, an operation is also performed. In the case of osteosynthetic treatment, plate osteosynthesis or marrow nailing is carried out. If there is an open fracture that is treated surgically, doctors often opt for a fixator.
Outlook & Forecast
The prognosis of a humeral shaft fracture is linked to the age of the patient and the severity of the fracture sustained. As you get older, the chance of a full recovery decreases steadily. Bone strength decreases over the course of life and damage to the skeletal system no longer regenerates completely.
With a slight fracture of the bone, the prognosis is favorable. With good medical care, the bones grow together so that there are no symptoms. Normally, the healing process lasts several weeks or months until the affected person’s body is fully resilient again.
If there is a complicated fracture with splintering, an operation is necessary. The bones are exchanged and the auxiliary parts needed to strengthen the bones are installed. If the operation proceeds without complications, the patient can move the arm sufficiently with a built-in intramedullary nail or fixation. The aids do not always achieve full functionality and resilience, but there is a significant improvement in health.
Failure to seek medical treatment can result in lifelong impairments and problems. The bones either don’t grow at all or grow together crookedly. As a result, a persistent restriction of the usual movement sequences and a low resilience are likely.
Prevention
A humeral shaft fracture cannot usually be prevented. It is advisable to avoid any indirect or direct acts of violence; however, since this is not always possible, no actual preventive measures can be recommended that will ultimately prevent a humeral shaft fracture.
Aftercare
In the case of a humeral shaft fracture, the person affected usually only has very limited measures or options for aftercare. However, these are not necessary either, since the humeral shaft fracture primarily requires medical treatment by a doctor in order to properly alleviate the symptoms. There are also no special complications, so that the course of the disease is usually positive.
As a rule, the life expectancy of those affected is not reduced by this disease. This injury is usually treated with a bandage or by plastering the affected area. The person concerned should take care not to unnecessarily burden the respective area and continue not to carry out any physical or strenuous activities. Sporting activities should also be avoided.
Furthermore, regular examinations and checks by a doctor are very important so that the humeral shaft fracture can heal properly. Early diagnosis is also of great importance. In some cases, the patients are restricted in their everyday life due to this disease and therefore also need help and support from their own family or from friends and acquaintances.
You can do that yourself
As a rule, the humeral shaft fracture cannot be treated by means of self-help. The broken bone is always treated by a doctor, with immobilization being the most important point of the treatment itself. There are no further complications and in most cases a complete healing occurs.
The affected person should be careful to wear the bandage or cast for several weeks as directed by the doctor and not take it off themselves. In some cases, surgical interventions may also be necessary if vessels have been damaged. Here, too, there are no options for self-help for those affected. By avoiding violent impacts, the humeral shaft fracture can generally be prevented. During the course of treatment, the affected region should not be unnecessarily strained, as this will slow down healing.
The affected person is severely restricted in their everyday life due to the humeral shaft fracture and often needs the help of other people. The help of friends or family has a very positive effect on the course of the disease. Talking to close friends is also very helpful in the case of psychological problems. As a rule, there is a positive course of the disease in the case of a humeral shaft fracture.