According to abbreviationfinder.org, a torn ligament is one of the most common sports injuries, along with stretching or straining the ligaments. Jerky movement and overuse of the ligaments can lead to ligament ruptures as a result of extreme physical activity. Known causes are therefore, for example, twisting the knee or twisting the foot. One of the most well-known tears of ligaments is the torn outer ligament on the upper ankle. The so-called cruciate ligament rupture can occur in the cruciate ligaments.
What is a torn ligament?
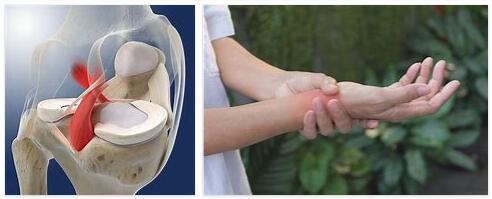
A torn ligament is a partial or complete tear in a joint ligament. The ligaments on the foot, ankle, knee, wrist, shoulder and elbow are most commonly affected. The thumb can also be affected by the torn ligament – this is known as the skier’s thumb.
A local and sometimes severe pain, combined with instability of the affected joint, is typical of a ligament tear. Also bruising occur frequently and cause swelling. There are four degrees of severity of ligament rupture. They range from an incomplete tear, in which the joint remains stable, to a complete ligament tear that destabilizes the joint.
Causes
A ligament tear occurs when a joint ligament is overstretched so much that its fibers are affected. Most of the time, this is the case with violent joint movements that involve excessive force on the ligaments – such as an abrupt twist. Joint ligaments consist of tight connective tissue, stabilize the joint and are usually extremely strong.
Too much stretching can damage the connective tissue – from the harmless sprain to a torn ligament. Such strong stretching occurs mainly during sports, which is why the ligament tear is considered a typical sports injury. A common example are balls that hit the joints hard, or even collisions by players, in which a joint is twisted and torn ligament. However, twisting the foot can also lead to ligament rupture.
At an unfavorable angle, a person’s body weight is sufficient to overload the joint ligaments. Multiple ligament ruptures are rare and are most likely to occur in car accidents.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
The torn ligament is one of the most common sports and movement injuries and usually occurs under stress and only in very rare cases from a state of rest. The torn ligament usually occurs in the knee area, in the area of the foot or shoulder, but all other areas of the body with ligaments can also be affected.
The torn ligament is felt by a strong pain. Usually there is an event before that, for example a twisting, a fall or a blow. Sometimes the tearing of a ligament can also be felt directly – the damaged ligament pulls back into the adjacent muscle; this type of rolling-up movement can sometimes be clearly felt.
The joint affected by the torn ligament can usually only be moved with great pain, and mobility is often completely limited at first. This is especially the case with tears, but can also be observed when there are tears. In most cases, the area around the affected joint swells visibly within a few minutes and feels hot, furry, and numb.
This remains the case during the healing process and only subsides completely over the course of several weeks. After a detailed diagnosis, the orthopedic surgeon decides whether the torn ligament needs to be operated on. Torn ligaments can partially regenerate themselves.
Course
In most cases, a torn ligament is noticeable at the moment of the actual tear: Many affected people hear a noise (often a pop or snap). At the same time, severe local pain occurs, which in most cases, however, subsides quickly despite the ligament rupture.
The mobility of the joint remains, however, which is often shown by an unsteady gait in the case of torn ligaments in the foot area. Swelling and bruising quickly appear. Since a torn ligament can be difficult to distinguish from sprains and strained ligaments, a doctor should be consulted if there is any suspicion. If untreated, a torn ligament can lead to chronic instability and damage to the joint.
Complications
Some instability may persist after a ligament rupture. For example, a knee may not regain its original stability after an operated cruciate ligament rupture. With a skier’s thumb, despite good treatment, slight restrictions in gripping may remain. If the ankle ligament ruptures, residual symptoms may persist.
The person concerned often underestimates the injury, continues to exercise and does not see a doctor despite the swelling and pain. In the long term, the torn ligament can cause problems and result in consequences. An insufficiently healed or undiscovered ski thumb can lead to permanent and painful instability. The so-called wobbly thumb is restricted in its movement, for example when grasping a ball.
If a torn ankle ligament is not adequately treated, permanent ligament stability can develop. The person concerned can – especially on uneven floors – keep kinking. A cruciate ligament tear that is not adequately treated can lead to recurrent knee pain and an unstable gait. In addition, injuries to the cartilage and / or meniscus can occur over the years. A torn ligament can also become chronic and lead to joint wear (osteoarthritis).
When should you go to the doctor?
A doctor must definitely be seen in the event of a torn ligament. In many cases, this complaint is an emergency that requires immediate attention to avoid further complications. As a rule, the doctor must be consulted if the person concerned complains of very severe and, above all, stabbing pain in a certain part of the body. These do not only occur during stress, but also in the form of pain at rest.
Bruising or swelling can also indicate the torn ligament and should definitely be examined. This is especially true if the symptoms occur after an accident or after strenuous sporting activity and do not go away on their own.
If the torn ligament is not treated, the joints can be damaged. An emergency doctor should therefore always be called after an accident or the hospital should be visited directly. If the symptoms do not occur acutely, a sports doctor can be consulted. Treatment is based on the severity of the crack.
Treatment & Therapy
If a ligament rupture is suspected, the so-called PECH rule should be used as first aid: break, ice, compression, elevation. The cooling, the pressure and the elevation reduce blood flow and pain. Then – even if the joint is painless – a doctor should be consulted to clarify the dimensions.
X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging are also used during the examination, depending on the region of the body. The joint stability is tested – if necessary under anesthesia, as severe pain can occur. Depending on the location and degree, the ligament tear is now either operated openly or minimally invasively or treated conservatively.
Conservative treatment is based primarily on consistent movement exercises and muscle training, but support bandages and, if necessary, a plaster cast can also be considered. If the torn ligament is treated conservatively, this usually takes eight weeks.
Outlook & forecast
With early diagnosis and treatment, the patient with a torn ligament has a good chance of recovery. The use of physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the success of the healing process.
Additionally, the prospect of complete healing depends on the type of injury. Depending on the severity, the course of the disease is more optimistic or less favorable. The injured ligament and the patient’s state of health must also be taken into account when making a prognosis. Adults with a healthy immune system, without previous illnesses and with a normal weight are often largely symptom-free after one to two weeks with good medical care. If the conditions are less favorable, it may take a few months for healing.
Fitness for sport is usually certified by a doctor after 3 months. It should be noted that permission to participate in intensive sports is only granted later and usually only with the use of joint protection. If the capsular ligaments are affected when the ligament ruptures, the healing process is delayed.
Nevertheless, with good medical care and the cooperation of the patient, freedom from symptoms is achieved within 3-6 months. The natural healing processes of the tissue last up to a year despite a certified recovery from a doctor. Patients also report increased sensitivity in the area for even longer.
Aftercare
A torn ligament is often underestimated, especially by athletes. The result is insufficient healing, even if the injury is operated on or treated. She needs a lot of patience and extensive aftercare, which can take months.
After the treatment, the doctor will order physiotherapy and, at the same time, a gentle way of dealing with the injured body part in everyday life. Sports activities should never be resumed too early, as there is a risk of tearing again. Physiotherapy exercises should also be started gently and only performed if they do not cause pain.
Usually the doctor and therapist will create a joint exercise plan. You will also decide when to start training. Starting too early can cause damage, while valuable time is wasted if the exercise is started too late. The aim of physiotherapy is to rebuild and strengthen the muscles that have been weakened by the torn ligament and the subsequent resting position.
If the foot is affected, the muscles of the leg should also be trained. Patients with a torn ligament therefore have to be patient and be careful with themselves in order to be completely healed and to be able to start training again.
You can do that yourself
A torn ligament is not a medical emergency. For example, if it happens in the middle of the night or while jogging on a remote forest path, there are a number of effective means of self-help.
First of all, it is usually important for the person affected to quickly relieve the pain caused by a torn ligament and to prevent swelling of the affected joint as much as possible. Both can be achieved through rapid cooling. If ice is used, care must be taken not to put it on the bare skin to avoid frostbite. It is important that the joint is not exposed to excessive heat such as direct sunlight.
The occurrence of a swelling can also be reduced by a quick bandaging. If you can already see a bruise, you can also use a heparin ointment. The bandage also serves to stabilize the joint. This is particularly important if it is not possible to take it easy at the beginning, because, for example, someone affected by a torn ligament in the ankle has to walk a few meters home.
Basically, the joint should be spared immediately after the ligament rupture. Ideally, the joint should be elevated. This also serves to counteract swelling and largely prevent any accumulation of blood in the injured area.